Space frame design methods. Good space frame design has the advantages of light weight, high stiffness, excellent seismic performance, convenient factory production, convenient installation, and can withstand uneven settlement of the foundation; the grid structure has strong adaptability and is suitable for large, medium and small spans. The support is flexible. It can adopt peripheral support and three-side support, four-point or multi-point support, and mixed support of peripheral support and point support.
The grid structure is widely used in my country, not only in public buildings such as gymnasiums, theaters, canteens, restaurants, but also in industrial buildings such as industrial workshop roofs. The advantages of the grid structure are listed in detail. This article is based on the basic form and selection of the grid structure of the steel structure, and provides some reference and help for space frame design beginners.
The selection of the space frame design should be comprehensively considered in combination with the plane shape, requirements, load and span size of the building, support conditions and economy. Usually we divide it according to the span size: large spans above 60m; medium spans from 30m to 60m; small spans below 30m.
1. Plane truss system
- Two-way orthogonal positive placement grid
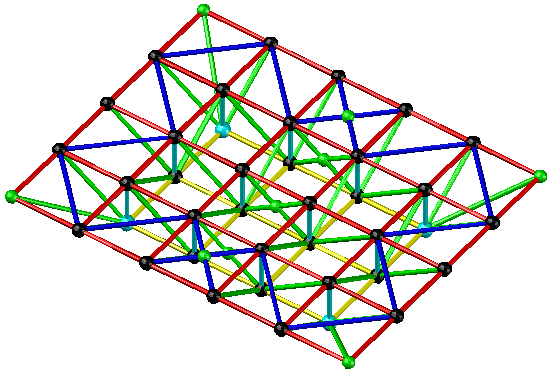

Applicable situation: Rectangular plane, peripheral support, side-to-length ratio less than 1.5, various spans can be used.
- Two-way orthogonal inclined grid
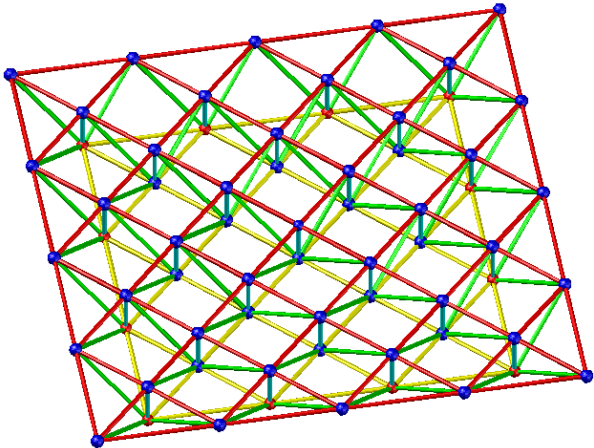

Applicable situation: Rectangular plane, peripheral support, side-to-length ratio less than 1.5, various spans can be used.
- One-way zigzag grid
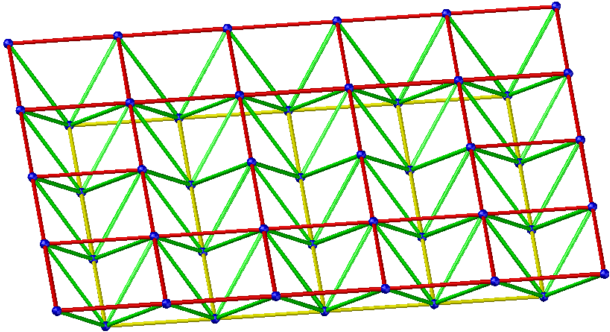

Applicable situation: Rectangular plane, peripheral support, side-length ratio greater than 2.
- Three-way grid
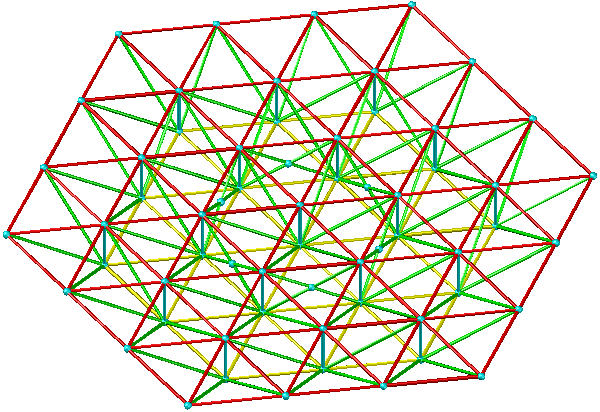

Applicable situation: It is suitable for circular or polygonal planes with regular grids around it, suitable for large-span projects.
2. Quadrangular pyramid system
- Positively placed quadrangular pyramid grid
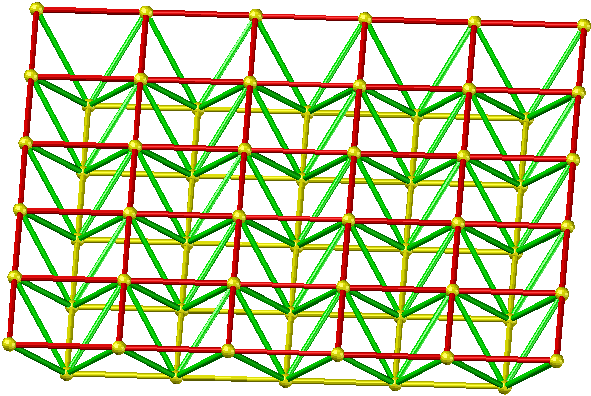

Applicable situation: It is suitable for the peripheral support grid with rectangular plane shape, the side-to-length ratio is less than 1.5, and the large-span project.
- Evacuated quadrangular pyramid grid
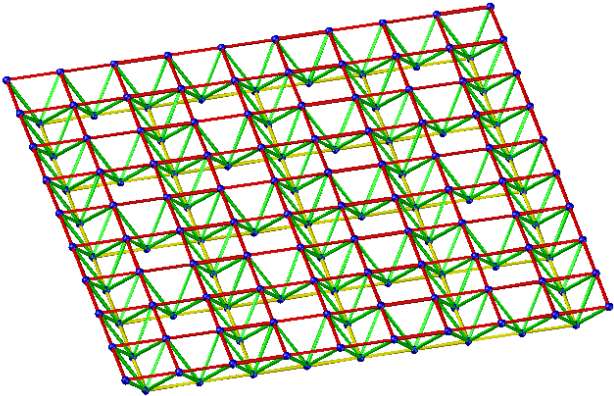

Applicable situation: It is suitable for the peripheral support grid with a rectangular plane shape. And the side-to-length ratio is greater than 1.5.
- Checkerboard-shaped quadrangular pyramid grid
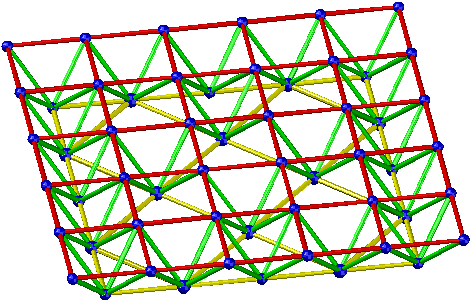

Applicable situation: It is suitable for the peripheral support grid with a rectangular plane shape, the side-to-length ratio is greater than 1.5, and the medium and small spans.
- Inclined quadrangular pyramid grid
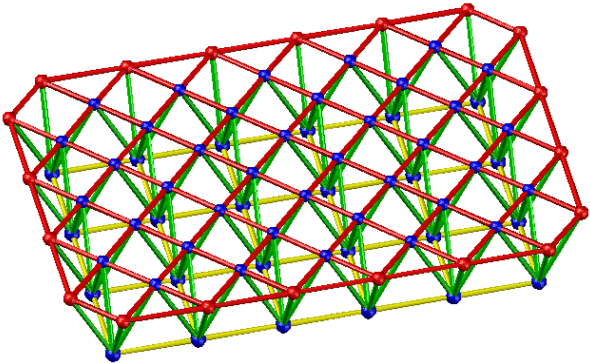

Applicable situation: It is suitable for the peripheral support grid with a rectangular plane shape. And the side-to-length ratio is greater than 1.5.
- Star-shaped quadrangular pyramid grid
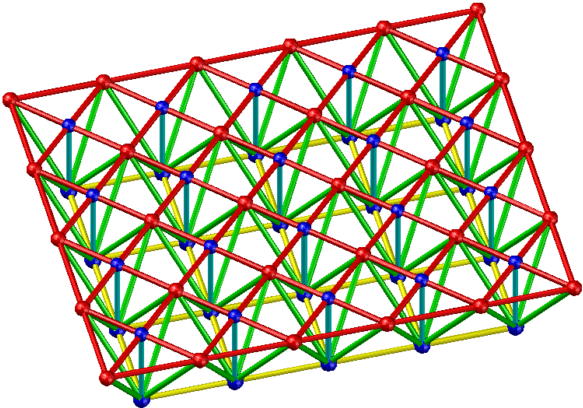

Applicable situation: It is suitable for the peripheral support grid with a rectangular plane shape, the side-to-length ratio is less than or equal to 1.5, and the medium and small spans.
3. Three, triangular pyramid system
- Triangular cone grid
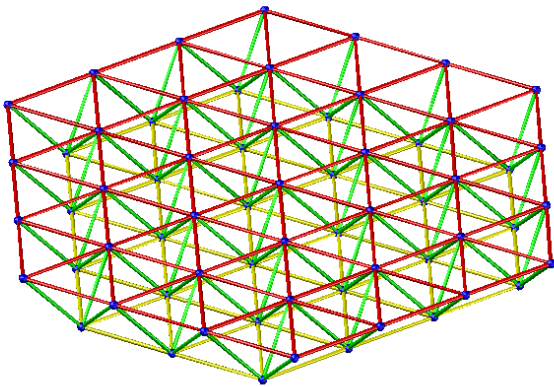

Applicable situation: It is suitable for the peripheral supporting grid frame with circular and polygonal plane shape. The side-to-length ratio is greater than 1.5, and the large-span project.
- Evacuate the triangular cone grid
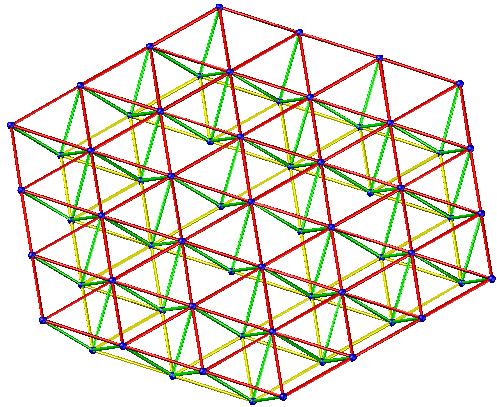

Applicable situation: It is suitable for the peripheral support grid with the plane shape of circle and hexagon. And the side-to-length ratio is greater than 1.5.
- Honeycomb triangular pyramid grid
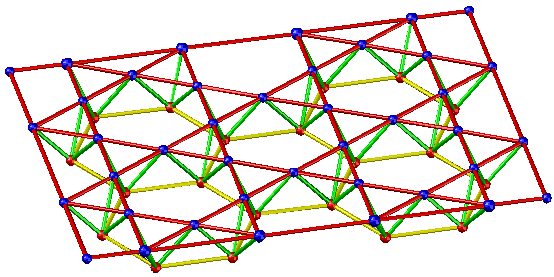

Applicable situation: It is suitable for the peripheral support grid with the plane shape of circle and hexagon. And medium and small spans is required.

